
Photo: ANDREWLOZOVYL/DepositPhotos
Doctors need to be skilled diagnosticians; however, future technologies are bound to aid them in determining the diseases their patients suffer from. Artificial intelligence offers vast possibilities within the medical field, promising to increase accuracy and decrease time spent on certain tasks. Lithuanian researchers have made a significant breakthrough. They trained an algorithm to examine fMRI brain scans and identify the early signs of Alzheimer’s Disease with an impressive accuracy of over 99%.
Alzheimer’s disease affects millions worldwide. A propensity for mental decline may show in brain scans well before external symptoms appear. Particularly, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is the step proceeding Alzheimer’s (although not all MCI leads to Alzheimer’s). Essentially, inside the brain the material may already be changing and atrophying. Doctors can examine an fMRI manually to note this change, but humans are less efficient than machines. As it turns out, they are likely less accurate, too.
The researchers at Kaunas Universities in Lithuania created an algorithm to search for evidence of Alzheimer’s changes in brain scans. They used deep-learning techniques, which means the algorithm was trained, tested, and refined based on a data set of 78,000 scans. Researcher Rytis Maskeliūnas commented, “Technologies can make medicine more accessible and cheaper. Although they will never replace the medical professional, technologies can encourage seeking timely diagnosis and help.” Doctors will still want to verify the results of the algorithm when it flags a troublesome scan. However, the algorithm would help eliminate human error by recommending certain scans for closer analysis.
Early flagging of potential Alzheimer’s disease offers patients more options. While there is not a technical cure for the disease, the more medicine understands about this heartrending prognosis, the more everyone can hope for better health outcomes.
A new algorithm uses artificial intelligence to identify the early signs of Alzheimer’s disease from fMRI brain scans.
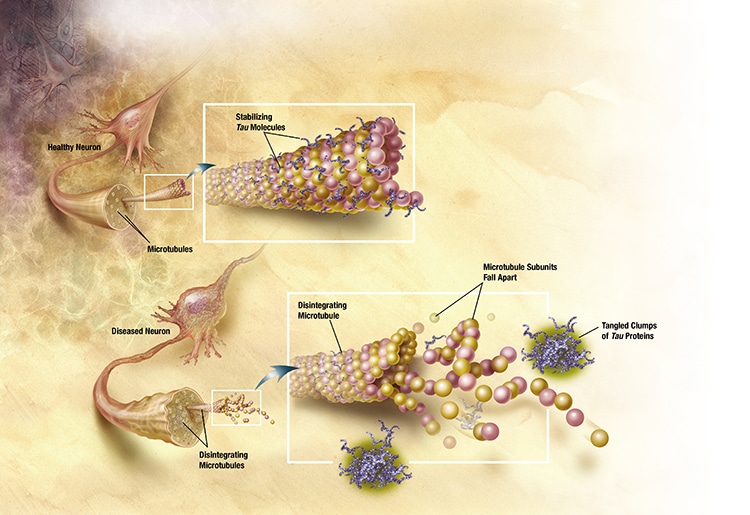
Diagram of mircotubules disintegrating with Alzheimer’s Disease. Tau proteins then form clumps. (Photo: Wikimedia Commons, Public domain)
h/t: [Science Alert]
Related Articles:
More and More Humans Have an Extra Artery, Proof of Ongoing Evolution
A Japanese Researcher Is Developing an Alzheimer’s Vaccine Which Can Be Taken Orally
Study Reveals How Much Exercise You Need To Counteract Sitting All Day Long
